Data Structures
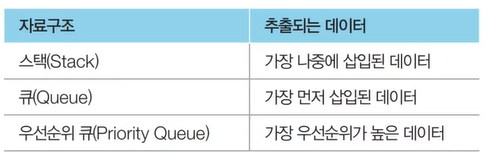
Stack
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the principle of Last In First Out (LIFO). This means the last element inserted inside the stack is removed first.
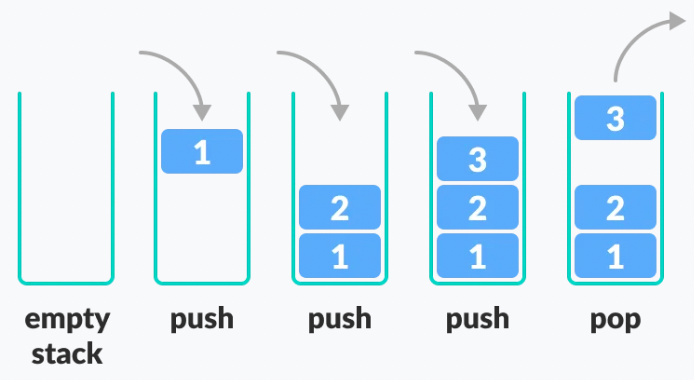
In the above image, although item 3 was kept last, it was removed first. This is exactly how the LIFO (Last In First Out) Principle works.
There are some basic operations that allow us to perform different actions on a stack.
- Push: Add an element to the top of a stack
- Pop: Remove an element from the top of a stack
- IsEmpty: Check if the stack is empty
- IsFull: Check if the stack is full
- Peek: Get the value of the top element without removing it
stack = []
stack.append(5)
stack.append(2)
stack.append(3)
stack.append(7)
stack.pop()
stack.append(1)
stack.append(4)
stack.pop()
print(stack[::-1]) #최상단 원소부터 출력 [1, 3, 2, 5]
print(stack) #최하단 원소부터 출력 [5, 2, 3, 1]
Time complexity
For the array-based implementation of a stack, the push and pop operations take constant time, i.e. O(1).
Applications
Although stack is a simple data structure to implement, it is very powerful. The most common uses of a stack are:
- To reverse a word - Put all the letters in a stack and pop them out. Because of the LIFO order of stack, you will get the letters in reverse order.
- In compilers - Compilers use the stack to calculate the value of expressions like
2 + 4 / 5 * (7 - 9)by converting the expression to prefix or postfix form. - In browsers - The back button in a browser saves all the URLs you have visited previously in a stack. Each time you visit a new page, it is added on top of the stack. When you press the back button, the current URL is removed from the stack, and the previous URL is accessed.
Queue
A queue is a useful data structure in programming. It is similar to the ticket queue outside a cinema hall, where the first person entering the queue is the first person who gets the ticket.
Queue follows the First In First Out (FIFO) rule - the item that goes in first is the item that comes out first.
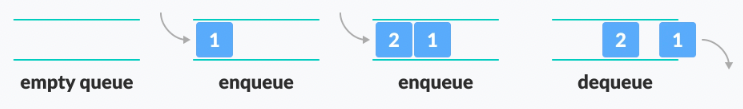
In the above image, since 1 was kept in the queue before 2, it is the first to be removed from the queue as well. It follows the FIFO rule.
- Enqueue: Add an element to the end of the queue
- Dequeue: Remove an element from the front of the queue
- IsEmpty: Check if the queue is empty
- IsFull: Check if the queue is full
- Peek: Get the value of the front of the queue without removing it
from collections import deque
queue =deque()
queue.append(5)
queue.append(2)
queue.append(3)
queue.append(7)
queue.popleft()
queue.append(1)
queue.append(4)
queue.popleft()
print(queue) #먼저 들어온 순서대로 출력 deque([3, 7, 1, 4])
queue.reverse()
print(queue) #나중에 들어온 원소부터 출력 deque([4, 1, 7, 3])
Time complexity
The complexity of enqueue and dequeue operations in a queue using an array is O(1). If you use pop(N) in Python code, then the complexity might be O(n) depending on the position of the item to be popped.
Applications
- CPU scheduling, Disk Scheduling
- When data is transferred asynchronously between two processes. The queue is used for synchronization. For example, IO Buffers, pipes, file IO, etc
- Handling of interrupts in real-time systems.
- Call Center phone systems use Queues to hold people calling them in order.
Priority Queue
A priority queue is a special type of queue in which each element is associated with a priority value. And elements are served on the basis of their priority. That is, higher-priority elements are served first.
- However, if elements with the same priority occur, they are served according to their order in the queue.
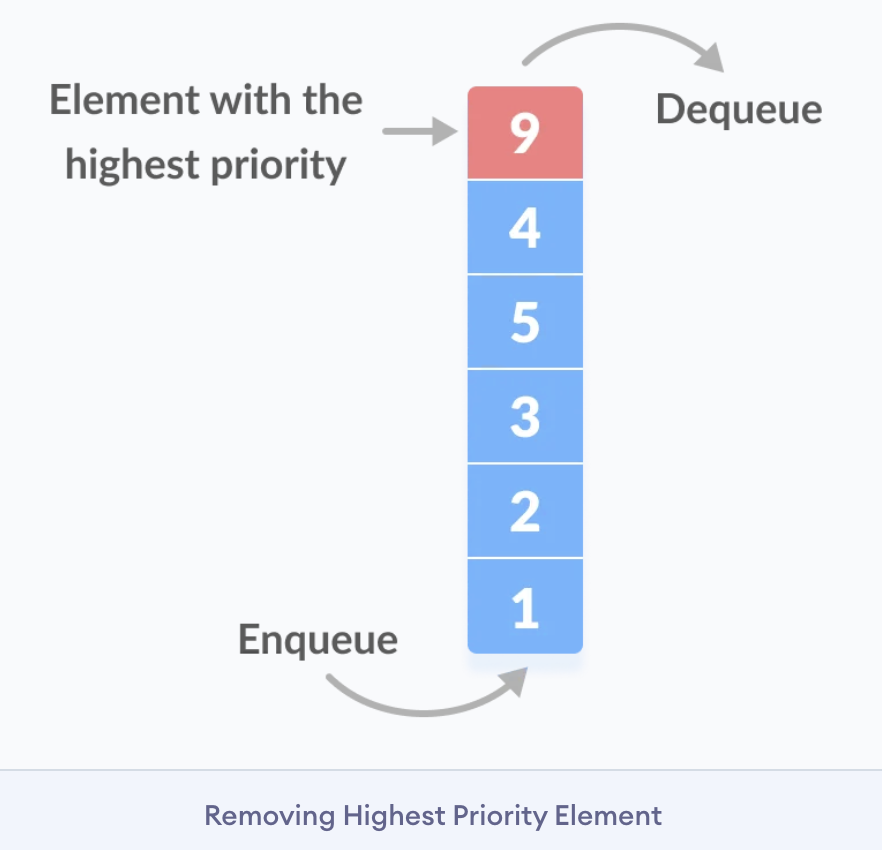
- 우선순위가 가장 높은 데이터를 가장 먼저 삭제하는 자료구조입니다.
- Python, C++, Java를 포함한 대부분의 프로그래밍 언어에서 표준 라이브러리 형태로 지원합니다.
Implementation of Priority Queue
Priority queue can be implemented using an array, ` a linked list, a heap data structure, or a binary search tree`. Among these data structures, heap data structure provides an efficient implementation of priority queues.
Hence, we will be using the heap data structure to implement the priority queue in this tutorial. A max-heap is implemented in the following operations. If you want to learn more about it, please visit max-heap and min-heap.
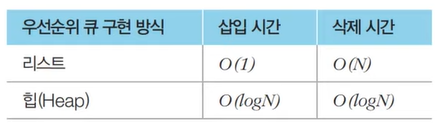
A comparative analysis of different implementations of priority queues is given below.
| Operations | peek | insert | delete |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linked List | O(1) |
O(n) |
O(1) |
| Binary Heap | O(1) |
O(log n) |
O(log n) |
| Binary Search Tree | O(1) |
O(log n) |
O(log n) |
Applications
Some of the applications of a priority queue are:
Dijkstra's algorithm- for implementing stack
- for load balancing and interrupt handling in an operating system
- for data compression in Huffman code
Heap Data Structure
Heap data structure is a complete binary tree that satisfies the heap property, where any given node is
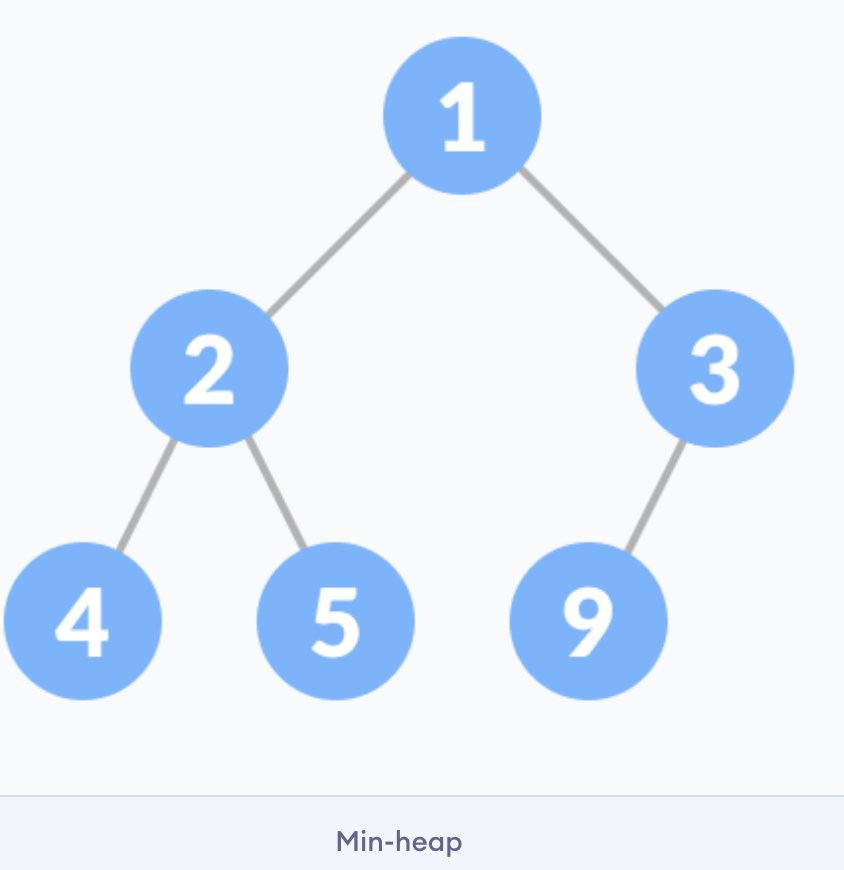
always greater than its child node/s, and the key of the root node is the largest among all other nodes. This property is also called max heap property. 부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드의 키 값보다 크거나 같은 완전 이진 트리always smaller than the child node/s, and the key of the root node is the smallest among all other nodes. This property is also called min heap property. 부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드의 키 값보다 작거나 같은 완전 이진 트리- 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)를 구현하기 위해 사용하는 자료구조 중 하나입니다.
- 최소 힙(Min Heap)과 최대 힙(Max Heap)이 있습니다.
Heap Operations
Heapify
Heapify is the process of creating a heap data structure from a binary tree. It is used to create a Min-Heap or a Max-Heap.
-
Let the input array be
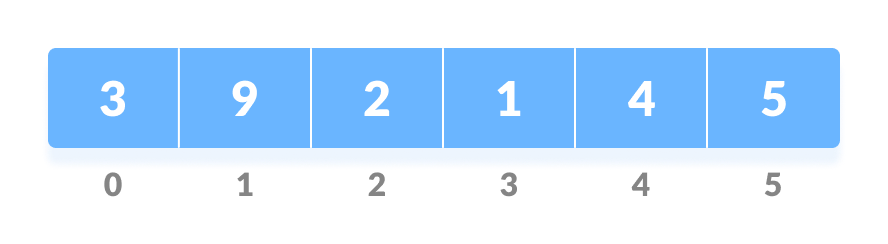 (Initial array).
(Initial array). -
Create a complete binary tree from the array
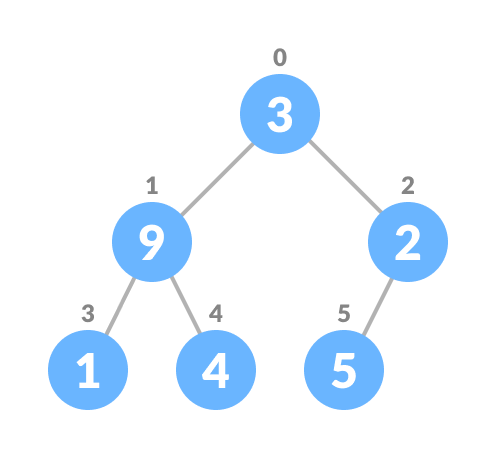 Complete binary tree.
Complete binary tree. -
Start from the first index of the non-leaf node whose index is given by
n/2 - 1= 6/2 - 1.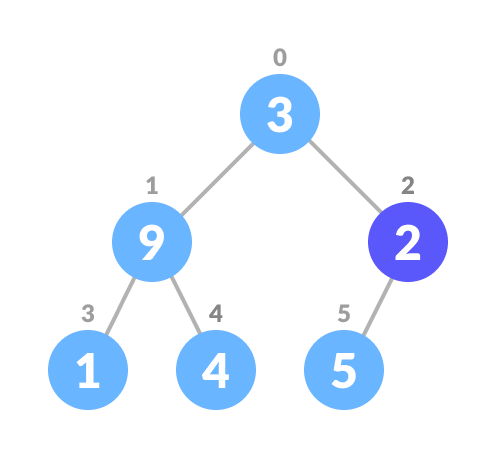 Start from the first leaf node
Start from the first leaf node -
Set current element
iaslargest. -
The index of left child is given by
2i + 1,and the right child is given by2i + 2. IfleftChildis greater thancurrentElement(i.e., element atithindex), setleftChildIndexas largest. IfrightChildis greater than element inlargest, setrightChildIndexaslargest. -
Swap
largestwithcurrent Element.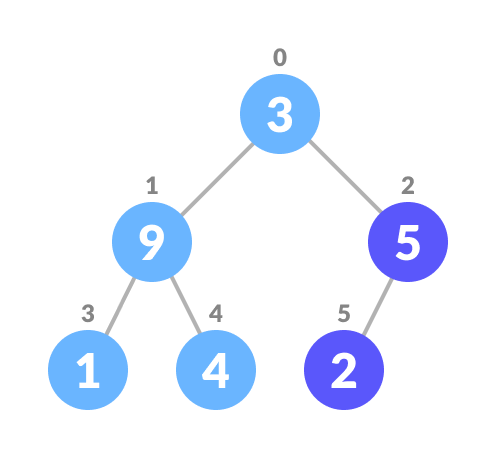 Swap if necessary
Swap if necessary -
Repeat steps 3-7 until the subtrees are also heapified.
Algorithm
Heapify(array, size, i)
set i as largest
leftChild = 2i + 1
rightChild = 2i + 2
if leftChild > array[largest]
set leftChildIndex as largest
if rightChild > array[largest]
set rightChildIndex as largest
swap array[i] and array[largest]
To create a Max-Heap:
MaxHeap(array, size)
loop from the first index of non-leaf node down to zero
call heapify
For Min-Heap, both leftChild and rightChild must be larger than the parent for all nodes.
Insert Element into Heap
-
Insert the new element at the end of the tree.
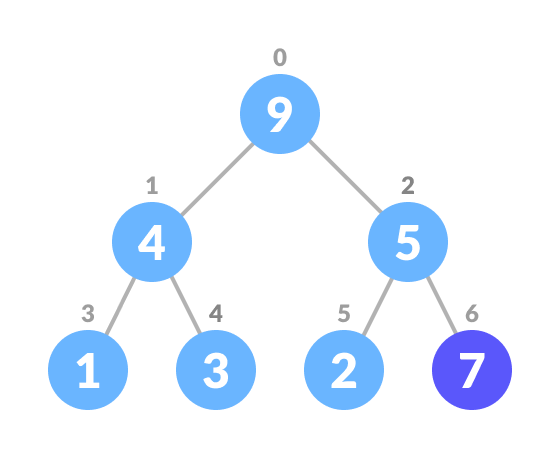
-
Heapify the tree.
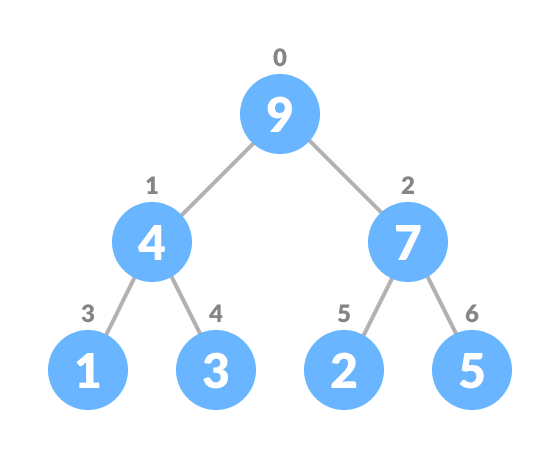
For Min Heap, the above algorithm is modified so that parentNode is always smaller than newNode.
Delete Element from Heap
-
Select the element to be deleted.
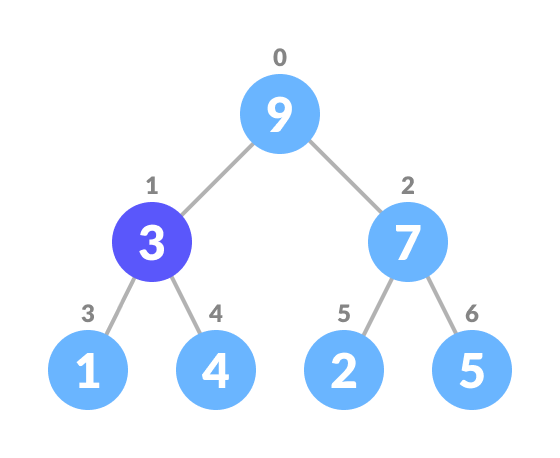
-
Swap it with the last element.
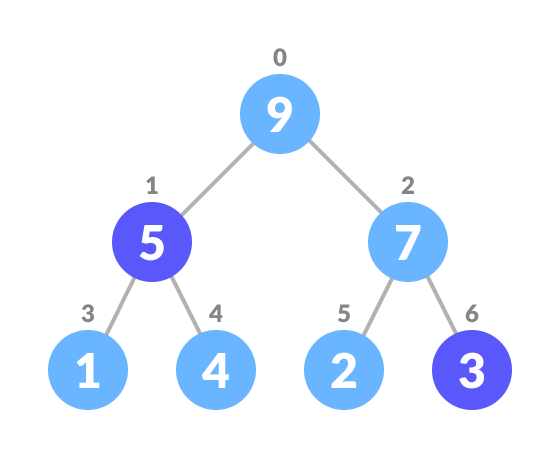
-
Remove the last element.
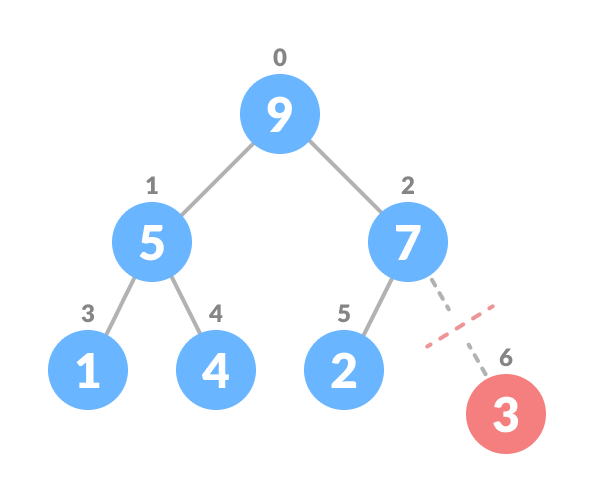
-
Heapify the tree.
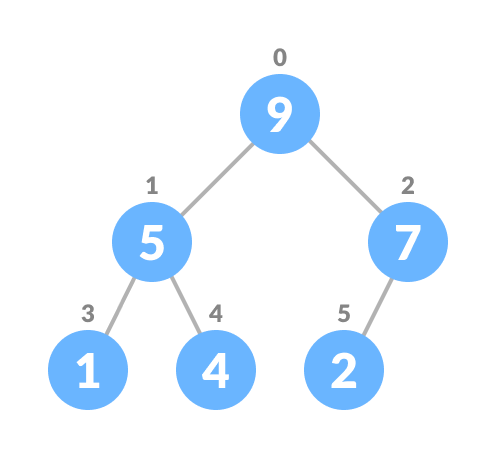 For Min Heap, the above algorithm is modified so that both
For Min Heap, the above algorithm is modified so that both childNodes are greater or smaller than currentNode.
Peek (Find max/min)
Peek operation returns the maximum element from Max Heap or minimum element from Min Heap without deleting the node.
For both Max Heap and Min Heap,
return rootNode
Extract-Max/Min
Extract-Max returns the node with maximum value after removing it from a Max Heap, whereas Extract-Min returns the node with minimum after removing it from Min Heap.
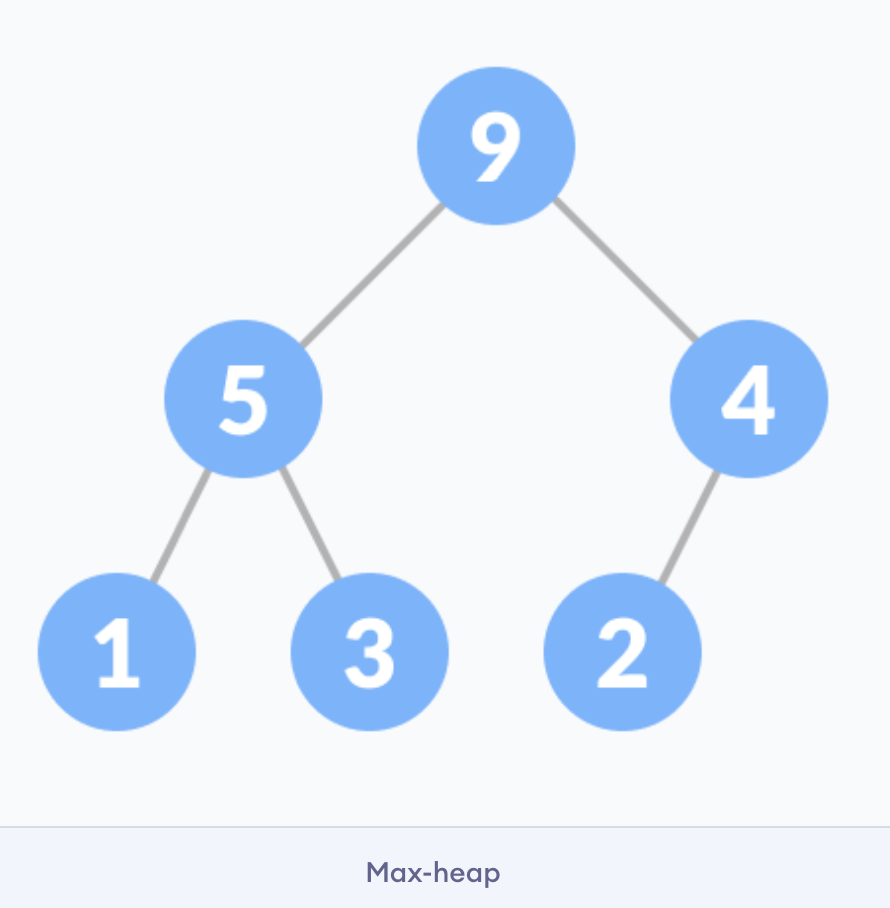
Max Heap and Min Heap
Max Heap
import heqpq
# 내림차순 힙 정렬(Heap Sort)
def heapsort(iterable):
h = []
result = []
# 모든 원소를 차례대로 힙에 삽입
for value in iterable:
heapq.heappush(h, -value)
# 힙에 삽입된 모든 원소를 차례대로 꺼내어 담기
for i in range(len(h)):
result.append(-heapq.heappop(h))
return result
result = heapsort([1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,0])
print(result)
[실행 결과]
[9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0]
Min Heap
import heapq
# 오름차순 힙 정렬(Heap Sort)
def heapsort(iterable):
h = []
result = []
# 모든 원소를 차례대로 힙에 삽입
for value in iterable:
heapq.heappush(h, value)
# 힙에 삽입된 모든 원소를 차례대로 꺼내어 담기
for i in range(len(h)):
result.append(heapq.heappop(h))
return result
result = heapsort([1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,0])
print(result)
[실행 결과]
[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
Applications
- Heap is used while implementing a priority queue.
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm
- Heap Sort
Leave a comment